RNA-based therapies are a powerful class of medicines derived from DNA or RNA that treat diseases by directly regulating gene activity. Technologies such as small interfering RNA (siRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), antisense oligonucleotides (ASO), and aptamers enable precise targeting of viral genes, disrupting their ability to replicate and spread. By addressing the root cause of infections at the genetic level, RNA drugs play a crucial role in developing effective treatments for infectious diseases, offering new solutions for outbreaks and global health challenges.
siRNA is a type of small RNA molecule that plays a key role in the regulation of gene expression. It is involved in a natural cellular process known as RNA interference (RNA), which serves to silence or downregulate specific genes.
siRNA molecules are typically 20-25 nucleotides long and are designed to be complementary to a target gene's messenger RNA (mRNA). When introduced into a cell, siRNA molecules specifically bind to the target mRNA, triggering its degradation or inhibiting its translation into a protein. This process can effectively "silence" the expression of the targeted gene, allowing researchers to study gene function or potentially develop therapeutic applications.
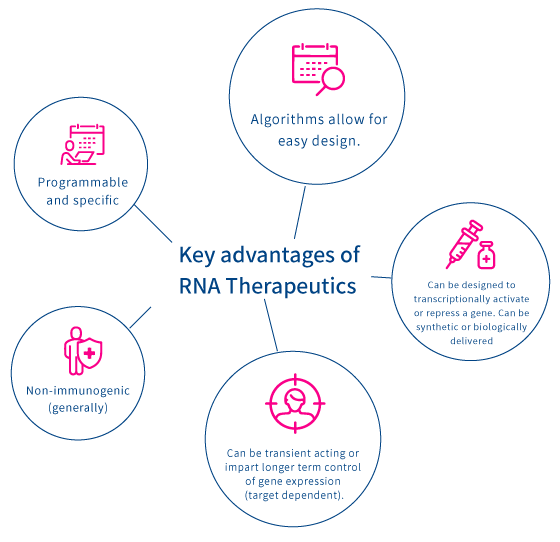
RNA technology has broad applications in research, including the study of gene function, the identification of potential drug targets, and the development of gene therapies to treat various diseases, including genetic disorders and certain types of cancer. Currently, our science team is developing siRNA drugs for COVID and seasonal influenza.
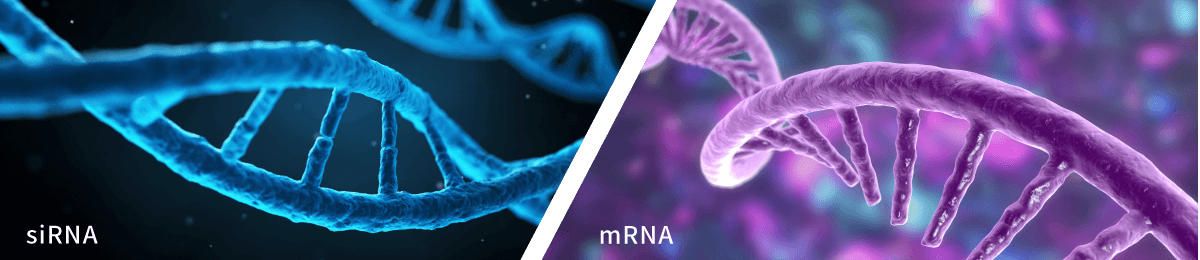
The key differences between mRNA (messenger RNA) and
siRNA (small interfering RNA) lies in their roles and functions within cells


In the world of genetics, small RNA molecules like siRNA and microRNA play a fascinating role in controlling gene activity. They can essentially turn genes on or off at different stages of gene expression, from the initial reading of the DNA code to the final protein production. This knowledge has profound implications for our understanding of gene regulation and provides a potential method for manipulating gene functions in the future. Small RNA molecules like siRNA have the incredible power to fine-tune gene expression in human cells. By targeting specific genes and regions, scientists can potentially harness this power for various applications in developing effective treatments for diseases.
The research team at Intelligene is dedicated to exploring how siRNA impacts gene expression. We are developing innovative siRNA drugs for precise treatments of infectious diseases. Our commitment is to unlock tomorrow's cures and enhance human health.

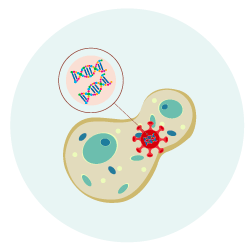
IG-001 and IG-002 are our first-in-class antiviral drugs targeted to SARS-CoV-2 and flu.
These RNA therapeutics target and degrade the viral RNAs inside the infected cell, essentially killing the virus.
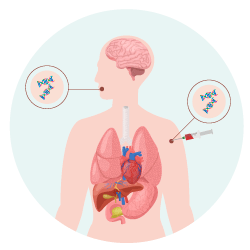
The siRNA-based therapeutics can be delivered a multitude of ways.
either inhaled,intravenous or via the skin with micro-needle patches